Stainless Steel Mesh Suppliers in Malaysia: A Sourcing Overview
Outline and Why Malaysia Matters for Stainless Steel Mesh
– Overview of the Malaysian stainless steel mesh market and regional relevance
– Product range, grades, and technical specifications buyers should know
– Supplier categories, capabilities, and how to compare offers objectively
– Quality assurance, certifications, and compliance checkpoints
– Sourcing strategy, pricing, logistics, and a practical conclusion
Malaysia sits at a strategic crossroads for metal fabrication and distribution in Southeast Asia, with modern port infrastructure, skilled processing talent, and established trade lanes to Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and the Americas. For buyers of stainless steel mesh—whether for filtration, enclosure, screening, architectural accents, food processing, aquaculture, or automotive—this geography reduces friction: components and raw coils flow in efficiently, while finished mesh rolls or cut-to-size panels ship out with predictable schedules. The nation’s participation in regional trade frameworks, combined with competitive manufacturing costs and solid technical capabilities, enables suppliers to serve both price-sensitive and precision-driven applications.
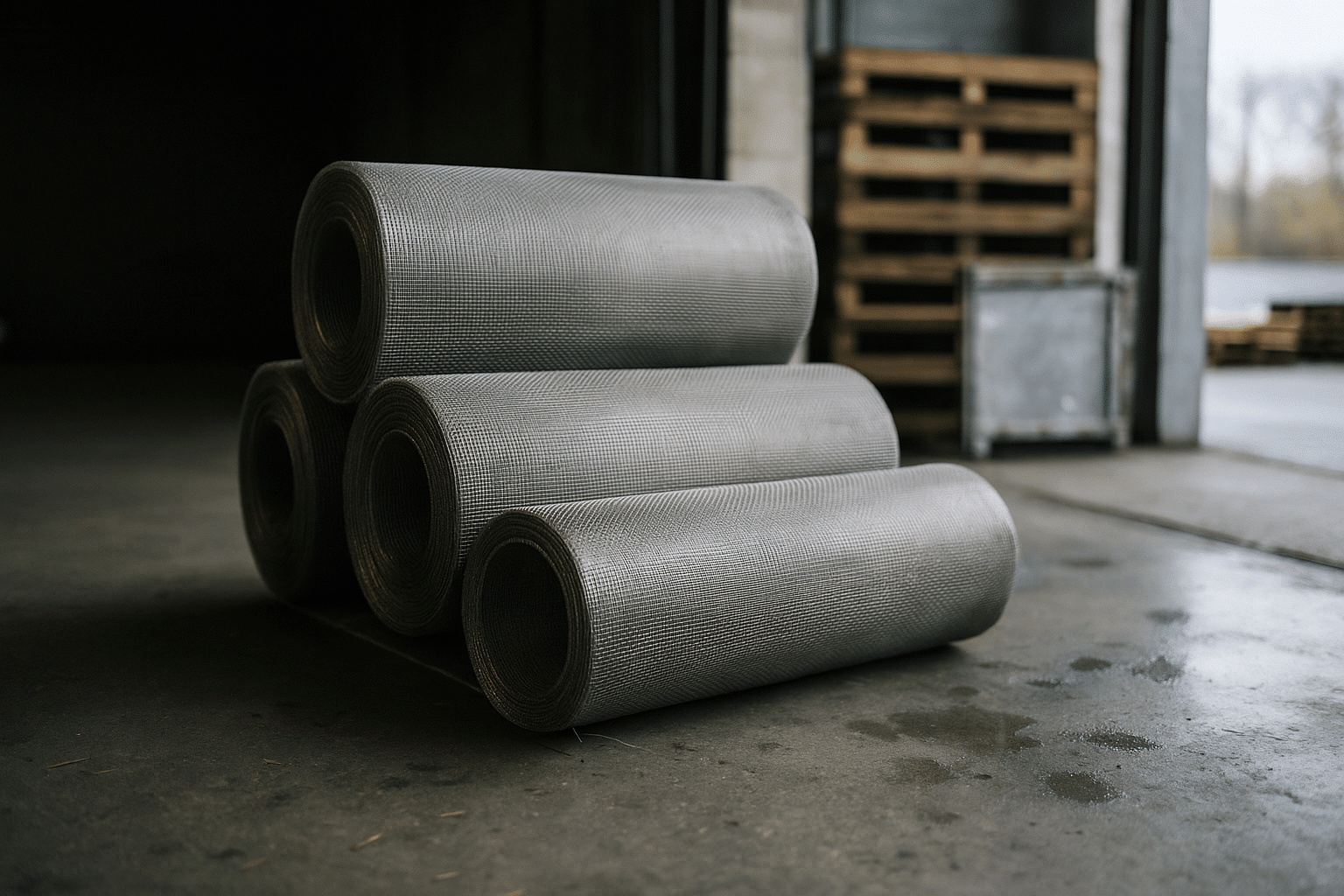
From a purchasing perspective, stainless steel mesh has a deceptively simple look yet a complex set of variables: grade selection (e.g., 304, 316, 316L), weave type (plain, twill, Dutch), mesh count, wire diameter, open area, finish, and packaging standards. Malaysia’s ecosystem includes vertically integrated producers, precision weavers, value-add fabricators, and stockists with wide inventories. This diversity gives buyers options for low minimum order quantities (MOQs), custom aperture designs, or quick-turn replenishment, depending on the project’s stage and budget. The key is to match your requirement to the right supplier profile and to document expectations clearly from the first RFQ onward.
Think of procurement here like plotting a reliable shipping lane: you identify your vessel (application), chart the route (specs and standards), pick the harbor (supplier type), and account for weather (quality and logistics risks). Done well, the result is mesh that arrives on time, meets dimensional and material specs, and installs without rework. The sections ahead provide a practical roadmap—complete with comparison points, QC checklists, and negotiation cues—to help you move from initial inquiry to repeatable supply.
Product Range, Grades, and Technical Specs Explained
Stainless steel mesh from Malaysia covers a broad spectrum, and clarity on specifications is the fastest route to consistent quality. Start with grade selection: 304 is widely used for general indoor applications; 316/316L enhances corrosion resistance for marine, chemical, or food-contact environments; duplex options are chosen for elevated strength or aggressive media. Buyers should consider the service environment, cleaning regimen, and mechanical loads when narrowing the grade. In coastal or chloride-rich conditions, 316/316L typically offers longer life due to molybdenum-enhanced corrosion resistance.
Weave and construction define the performance envelope. Common formats include:
– Plain weave: balanced strength and flow, suited for general filtration and screening.
– Twill weave: allows thicker wires for the same mesh count, improving robustness.
– Dutch and reverse Dutch weave: tailored for fine filtration with asymmetric flow profiles.
– Welded mesh: fusion-welded intersections for rigidity in fencing, guards, and cages.
– Expanded stainless mesh: slit-and-stretched, creating diamond openings for ventilation and architectural panels.
Technical parameters deserve precise notation on your drawings and purchase orders. At minimum, specify:
– Mesh count or aperture size (e.g., openings per inch or microns).
– Wire diameter with tolerance (e.g., ±0.01 mm).
– Open area percentage, if airflow or filtration rate matters.
– Roll width/length or sheet size, including edge conditions (trimmed, selvedge).
– Finish and surface treatment (mill finish, pickled and passivated).
– Flatness and camber limits for sheets, and spool tension guidelines for rolls.
Reference standards help align expectations. Buyers frequently cite ISO 9044 (woven wire cloth) and ASTM E2016 for dimensional tolerances, while ASTM A240 relates to stainless plate/sheet material requirements used for wire production. For surface cleanliness and corrosion performance, request evidence of passivation in line with ASTM A967, and where relevant, documentation that supports food-contact suitability (e.g., compliance with recognized hygiene practices for indirect contact). Packaging also matters more than it appears: export-grade wrapping with moisture barriers, desiccants, reinforced cores, and edge protectors reduces transit damage, especially when shipments move through humid or tropical climates.
Finally, consider downstream processing. If the mesh will be cut, formed, spot-welded, or framed, clarify permissible heat tint, discoloration removal, and protective films. Small details—like the direction of the weave relative to the frame or the intended expansion side for expanded mesh—can make installation seamless. By codifying these points early, you transform a commodity purchase into a controlled specification that suppliers can quote and manufacture consistently.
Supplier Landscape in Malaysia: Types, Capabilities, and Comparisons
Malaysia’s supplier base can be grouped into complementary categories, each serving different priorities for cost, lead time, and customization. Understanding these archetypes helps you shortlist faster and negotiate more effectively.
Typical supplier types include:
– Integrated producers: control wire drawing, weaving, and finishing in-house; suitable for consistent volume, tighter traceability, and bespoke specs.
– Precision weavers: focus on tight tolerances, specialty weaves, and small apertures; often chosen for filtration, laboratory, and process-critical uses.
– Fabricators and value-add shops: provide cutting, framing, forming, and spot welding; ideal for ready-to-install panels or assemblies.
– Stockists and traders: maintain breadth of inventory and rapid dispatch; useful for maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) needs or urgent replenishment.
– OEM-focused partners: configure private-label packaging, documentation, and batch coding aligned to your internal systems.
Geography also influences capabilities. The Klang Valley typically hosts a cluster of distributors and fabricators with strong logistics access to major ports. Industrial zones in Johor benefit from proximity to cross-border routes and established metalworking ecosystems. Penang and northern corridors often emphasize precision manufacturing supported by electronics and medical device supply chains. These regional nuances translate into practical differences—lead time flexibility, available finishing options, or ability to coordinate multi-supplier assemblies.
When comparing offers, evaluate beyond unit price. Consider:
– Process capability: repeatability of mesh count, wire diameter, and open area.
– Documentation: completeness of MTRs, heat number traceability, and inspection reports.
– Change management: responsiveness to engineering revisions and nonconformance handling.
– Capacity signals: stated monthly output, available loom widths, and typical MOQs.
– Communication cadence: proactive updates during weaving, finishing, and packing.
Lead times vary by complexity. Off-the-shelf welded mesh may ship in days, while fine Dutch weaves with narrow tolerances can require weeks for loom setup, validation, and passivation. If your project timeline is tight, ask suppliers to outline a production Gantt—loom allocation, drawing, weaving, inspection, finishing, and dispatch milestones—so you can spot risks early. For sustained programs, dual-sourcing across two categories (e.g., one precision weaver and one stockist) balances depth with agility.
Ultimately, the right Malaysian partner is the one whose core strengths align with your critical-to-quality attributes. By mapping your priorities—speed, precision, customization, or downstream fabrication—to the appropriate supplier type, you anchor negotiations in fit rather than purely on price.
Quality Assurance, Standards, and Compliance: Building Confidence
Quality in stainless steel mesh is a combination of metallurgy, geometry, and surface condition, all governed by clear standards and disciplined inspection. Start with the material pedigree. A complete material test report should verify chemical composition for the specified grade, including chromium, nickel, and—where applicable—molybdenum content. Heat numbers must be traceable to each batch of wire used in weaving or welding, and lot identification should travel from raw coil to finished roll or panel.
Dimensional accuracy determines function in filtration and screening. A robust inspection plan covers:
– Mesh count and aperture measurements using calibrated optical methods.
– Wire diameter checks at statistically relevant sample sizes.
– Open area calculations validated against measured data.
– Flatness, warp, and weft alignment confirmation for woven mesh.
– Weld integrity spot checks (for welded mesh) using shear or peel assessments.
Standards provide common language. ISO 9044 and ASTM E2016 outline tolerances for woven wire, while ISO 7800/7801 can guide mechanical property tests on wire. For corrosion performance, salt spray per ASTM B117 can help compare finishes, though buyers should interpret results in context as stainless performance in service depends on environment, finish, and maintenance. Passivation to ASTM A967 improves corrosion resistance by restoring the chromium-rich oxide layer after fabrication. If the mesh touches food or pharmaceuticals, request documentation aligned with recognized hygiene and contact expectations, and ensure surfaces are free from embedded contaminants or polishing residues.
Document control and sampling discipline prevent drift over time. Many Malaysian suppliers maintain certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management; ask for current certificates and scope details. Use sampling plans (e.g., ANSI/ASQ Z1.4) to set acceptance levels tailored to your risk tolerance. Practical QC deliverables might include incoming inspection checklists, photos of loom setups, in-process gauge readings, and final inspection reports with measurable metrics, not just pass/fail marks.
Packaging quality is the last line of defense. Specify:
– Moisture barriers and desiccants for tropical shipping routes.
– Edge guards and reinforced cores to prevent crush damage.
– Clear labels with grade, mesh count, aperture, wire diameter, lot number, and net weight.
– Sealed, clean wrapping for food-oriented applications.
By aligning supplier controls with your internal quality plan—and by auditing once or twice per year—you create a feedback loop that drives continuous improvement, reduces nonconformances, and keeps total cost of ownership in check.
Sourcing Strategy, Pricing, Logistics, and Actionable Conclusion
Effective sourcing combines clear specifications with an honest assessment of total cost. Begin with a structured RFQ that requests: grade, weave type, mesh count or aperture, wire diameter and tolerance, open area, roll/sheet dimensions, finish and passivation, packaging, inspection documentation, and delivery terms. Ask for unit price breaks at multiple quantities, loom setup fees (if any), MOQs, standard lead times, and options for expedited production. Encourage suppliers to propose alternates—such as nearby wire diameters or standard roll widths—that might reduce scrap or increase yield without compromising function.
Price is only one component of landed cost. Evaluate:
– Incoterms: FOB Port Klang or Penang vs. CIF to your port; choose based on freight control preference.
– Freight: consider consolidation to optimize container utilization; moisture-sensitive cargo benefits from dehumidifier packs.
– Duties and taxes: check your country’s tariff schedule; some trade agreements can lower or eliminate duties.
– Currency risk: quotes may be in MYR or USD; lock in rates or include buffers if exposure is material.
– Quality costs: factor in inspection time, potential rework, and supplier audit expenses.
To visualize impact, build a simple model: start with unit price, add inland transport to port, ocean/air freight, insurance, duties, brokerage, and local delivery. Divide by usable square meters or panels after expected scrap, and compare suppliers on a per-functional-unit basis. When two quotes are close, the tie-breaker often comes from quality assurance depth, lead-time reliability, and communication transparency.
Logistics planning reduces surprises. Clarify export documents needed: commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and inspection reports. For time-sensitive projects, align production completion with vessel schedules and ask for pre-shipment photos of packaging and labels. If your application is critical, consider a small pilot batch followed by a ramp-up to validate performance in real conditions. Dual-sourcing across two qualified Malaysian suppliers—or pairing one Malaysian source with another regional option—adds resilience against capacity constraints or unforeseen disruptions.
Conclusion for buyers: Malaysia offers a well-rounded mesh ecosystem—capable precision weaving, dependable finishing, and efficient ports—that can support both prototype agility and program scale. Define your requirements tightly, compare suppliers on capability and documentation rather than unit price alone, and manage logistics with the same rigor you apply to specifications. Do this, and you turn a routine purchase into a controlled, auditable supply stream that delivers consistent performance over time. Your next step is simple: assemble a clear RFQ package, shortlist two to three supplier types that fit your priorities, and pilot a batch to validate the partnership before you scale.